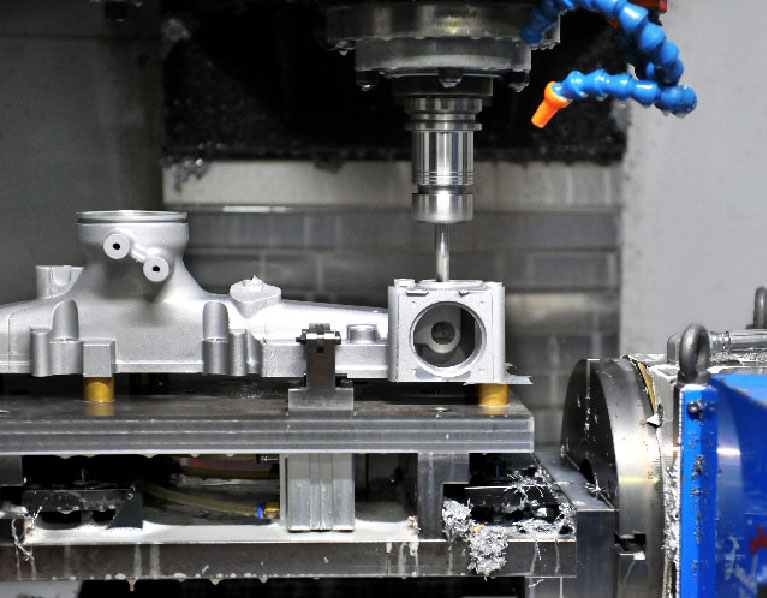
Prototype die casting is a crucial manufacturing process that enables businesses to create high-quality metal prototypes with precision and efficiency. It is widely used across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods to test and validate product designs before full-scale production. By leveraging aluminum die cast prototypes, manufacturers can evaluate the strength, durability, and functionality of their designs while minimizing production costs and time-to-market. Die casting prototypes are essential in modern engineering, allowing companies to refine their products and address potential design flaws before committing to large-scale manufacturing. With advancements in die casting technology, prototype manufacturing has become faster, more cost-effective, and more adaptable to complex geometries. This article explores the benefits, process, applications, and challenges of prototype die casting, highlighting why it remains a preferred choice for metal prototype production.
Understanding Prototype Die Casting
Prototype die casting is a process where molten metal, typically aluminum, zinc, or magnesium, is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure to create detailed and accurate metal parts. Unlike traditional machining or 3D printing, die casting offers exceptional consistency and strength, making it an ideal solution for producing prototypes that closely resemble final production parts. The primary goal of prototype die casting is to test a product’s design, performance, and manufacturability before mass production. Since die casting produces parts with tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes, engineers can evaluate the prototype’s functionality without the need for extensive post-processing.
Advantages of Aluminum Die Cast Prototypes
Aluminum die cast prototypes are widely used in various industries due to the unique properties of aluminum. Some key advantages of using aluminum in prototype die casting include:
- Lightweight and Strong: Aluminum provides an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for applications where weight reduction is essential, such as automotive and aerospace components.
- High Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum’s ability to conduct heat and electricity efficiently makes it ideal for electrical enclosures and heat sink applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum die cast prototypes have natural corrosion resistance, ensuring durability in harsh environments.
- Complex Geometries: Die casting allows for the production of intricate and detailed parts that are difficult to achieve with other prototyping methods.
- Cost-Effective Production: Once the mold is created, aluminum die casting enables rapid and repeatable production of prototypes at a relatively low cost compared to CNC machining.
These advantages make aluminum die cast prototypes an excellent choice for industries that require high-performance and lightweight components.
The Die Casting Prototyping Process
The die casting prototyping process consists of several critical steps, ensuring that the final prototype meets design specifications and quality standards. The typical process includes:
- Design and Mold Preparation: Engineers create a 3D model of the prototype and develop a mold using durable materials such as steel. The mold is designed to withstand high temperatures and pressure.
- Melting and Injection: The chosen metal, often aluminum, is melted in a furnace and injected into the mold cavity at high pressure. This ensures that the molten metal fills all intricate details of the mold.
- Cooling and Solidification: The metal cools and solidifies quickly inside the mold, retaining the desired shape and structural integrity.
- Ejection and Finishing: Once the prototype is solidified, it is ejected from the mold. Secondary processes such as trimming, machining, and surface finishing may be performed to achieve the final specifications.
- Quality Inspection: The prototype undergoes thorough inspection and testing to verify dimensions, material properties, and overall performance.
This streamlined process allows manufacturers to develop high-quality die casting prototypes quickly, making it an efficient method for testing new product designs.
Applications of Die Casting Prototypes
Die casting prototypes are utilized across multiple industries, playing a critical role in product development and innovation. Some key applications include:
- Automotive Industry: Aluminum die cast prototypes are commonly used to develop lightweight engine components, transmission housings, and structural parts to enhance fuel efficiency and performance.
- Aerospace Sector: Die casting prototypes help create aircraft components that require strength, precision, and resistance to extreme temperatures.
- Consumer Electronics: Many electronic devices feature die-cast aluminum enclosures for protection against heat and impact. Prototyping ensures proper fit and functionality before mass production.
- Medical Equipment: Die casting prototypes are used in medical devices, ensuring high precision and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Industrial Machinery: Prototype die casting helps manufacturers develop durable and high-performance components for industrial machinery and tools.
With such diverse applications, die casting prototypes continue to be a vital component in product development and testing.
Challenges in Prototype Die Casting
Despite its many advantages, prototype die casting comes with some challenges that manufacturers must consider:
- Initial Tooling Costs: Creating a mold for die casting prototypes can be expensive, especially for small production runs. However, this cost is offset when producing multiple prototypes or transitioning to full-scale manufacturing.
- Design Limitations: While die casting is excellent for producing complex shapes, some extreme geometries may require additional machining or modifications to achieve the desired results.
- Material Constraints: Some materials used in die casting, such as aluminum and zinc, have specific properties that may not be suitable for all applications. Engineers must carefully select the right material for their prototypes.
- Porosity Issues: If not properly managed, trapped air during the casting process can lead to porosity, affecting the mechanical properties of the prototype. Advanced casting techniques help reduce porosity and improve part quality.
By addressing these challenges through proper design, material selection, and process optimization, manufacturers can maximize the benefits of prototype die casting.
How to Choose the Right Die Casting Prototype Partner
Selecting the right manufacturing partner for die casting prototypes is essential for achieving high-quality results. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a prototype die casting provider:
- Experience and Expertise: Look for a company with a strong track record in die casting and prototyping. Experienced manufacturers understand the intricacies of the process and can provide valuable design insights.
- Advanced Technology: Ensure the manufacturer uses state-of-the-art die casting equipment and software for precise and efficient production.
- Material Options: A good die casting partner should offer a variety of materials, including aluminum, zinc, and magnesium, to suit different application needs.
- Rapid Turnaround Times: Choose a provider that can deliver high-quality die casting prototypes within tight deadlines to accelerate your product development cycle.
- Quality Assurance: Look for a manufacturer with robust quality control measures, including dimensional inspections and material testing, to ensure consistent and reliable prototypes.
By selecting a reliable die casting partner, businesses can streamline the prototyping process and bring their products to market faster with confidence.
It looks like the article has already covered the essential aspects of prototype die casting, including its advantages, process, applications, challenges, and selecting the right manufacturing partner. However, I can expand on additional areas related to prototype die casting to enhance the depth of the article.
Innovations in Prototype Die Casting
The die casting industry is continuously evolving with new technologies and materials that improve efficiency, precision, and sustainability. Some of the most notable innovations include:
1. 3D Printing for Die Casting Tooling
Traditional die casting requires expensive tooling and molds, which can take weeks or months to manufacture. However, advancements in 3D printing have significantly reduced lead times and costs by allowing manufacturers to create rapid tooling inserts. 3D-printed molds, made from high-strength materials, provide a cost-effective way to produce small batches of die casting prototypes before committing to expensive steel molds.
2. Vacuum-Assisted Die Casting
One of the challenges in die casting is porosity, which occurs when air gets trapped inside the molten metal during injection. Vacuum-assisted die casting is an innovation that minimizes porosity by removing trapped air, resulting in stronger and more reliable prototypes. This technology is particularly beneficial in aerospace and automotive industries, where structural integrity is critical.
3. Semi-Solid Die Casting (SSM Process)
Semi-solid die casting is an advanced technique that involves injecting metal in a semi-solid state rather than a fully molten state. This process enhances the mechanical properties of the die cast prototype, reduces shrinkage defects, and improves dimensional accuracy. Aluminum die cast prototypes made using the SSM process exhibit superior strength and reduced porosity.
4. High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) Advancements
High-pressure die casting (HPDC) is the most common method for manufacturing die casting prototypes. Recent developments in HPDC technology have led to better thermal management, improved mold designs, and automated production lines. These advancements ensure faster cycle times, increased repeatability, and better surface finishes for aluminum die cast prototypes.
Environmental Considerations in Die Casting Prototyping
Sustainability has become a major focus in the manufacturing industry, including die casting prototyping. Several initiatives are being adopted to make prototype die casting more environmentally friendly:
- Recycling Aluminum and Other Metals: Aluminum is one of the most recyclable materials in the world, and many die casting facilities now use recycled aluminum to reduce waste and energy consumption.
- Energy-Efficient Casting Machines: Modern die casting machines are designed to consume less energy while maintaining high performance. These machines use advanced heating and cooling systems to optimize energy use.
- Eco-Friendly Coatings and Lubricants: Traditional die casting requires lubricants and coatings that can contain harmful chemicals. New eco-friendly alternatives are now available that minimize environmental impact without compromising part quality.
- Waste Reduction Strategies: Many die casting manufacturers implement waste reduction programs by reusing excess material and adopting lean manufacturing principles to optimize production efficiency.
By incorporating these sustainability practices, die casting prototyping is becoming more environmentally responsible while maintaining its effectiveness as a critical manufacturing process.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Die Casting Prototypes
Many industries have successfully leveraged die casting prototypes to accelerate product development and improve manufacturing efficiency. Here are a few real-world examples:
Automotive Industry: Lightweight Engine Components
A leading automotive manufacturer needed to develop a lightweight yet durable engine component for an upcoming fuel-efficient vehicle. Using aluminum die cast prototypes, the company was able to test different designs and optimize the part for better heat dissipation and weight reduction. The final prototype passed rigorous testing and was approved for mass production, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Aerospace Industry: High-Precision Structural Parts
An aerospace company required high-precision aluminum die cast prototypes for a new aircraft design. By using vacuum-assisted die casting, the company was able to achieve minimal porosity and high structural integrity. The prototypes underwent extensive stress testing, ensuring they met stringent safety and performance standards before transitioning to large-scale production.
Consumer Electronics: Durable Smartphone Casings
A consumer electronics brand wanted to design a sleek yet durable smartphone casing using aluminum die casting. The prototyping phase allowed engineers to experiment with different surface finishes, thermal conductivity properties, and durability factors. The final design provided an optimal balance of aesthetics and functionality, resulting in a successful product launch.
Future Trends in Prototype Die Casting
As technology continues to evolve, the future of prototype die casting looks promising. Several trends are shaping the industry:
1. Increased Automation in Die Casting
Automation is playing a major role in die casting prototype production. Robots and AI-powered systems are being integrated into die casting facilities to enhance precision, reduce human error, and speed up production cycles. Automated die casting also improves worker safety by reducing direct exposure to high temperatures and molten metal.
2. Hybrid Manufacturing Approaches
A combination of die casting and additive manufacturing (3D printing) is being explored to create hybrid prototypes. This approach allows manufacturers to 3D print complex features onto die-cast parts, combining the best of both technologies for enhanced performance.
3. Smart Die Casting with IoT Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing manufacturing by enabling real-time monitoring of die casting machines and processes. Smart sensors collect data on temperature, pressure, and material flow, allowing manufacturers to optimize operations and reduce defects in prototype production.
4. New Die Casting Materials
While aluminum remains the dominant material for die casting prototypes, new alloys with enhanced properties are being developed. Magnesium, for example, offers even greater weight savings, while advanced aluminum-zinc alloys provide improved strength and corrosion resistance. These new materials will expand the capabilities of die casting in various industries.
Conclusion
Prototype die casting continues to be a vital manufacturing process for companies looking to develop high-quality metal prototypes efficiently. Aluminum die casting prototypes offer numerous advantages, including lightweight construction, durability, and cost-effective production. The process enables businesses to test and refine their designs before committing to full-scale manufacturing, reducing the risks of costly errors. With advancements in die casting technology, automation, and sustainability practices, the future of die casting prototypes looks even more promising. Companies that leverage modern die casting techniques will gain a competitive edge by accelerating product development, reducing production costs, and enhancing overall product quality.
By understanding the benefits, challenges, and future trends of prototype die casting, businesses can make informed decisions and optimize their manufacturing processes. As industries continue to innovate, die casting prototypes will remain an essential tool for bringing cutting-edge products to market faster and more efficiently. Prototype die casting is an essential process for industries that require high-quality metal prototypes with precision and durability. Aluminum die cast prototypes offer significant advantages, including lightweight construction, corrosion resistance, and cost-effective production. The die casting prototyping process allows manufacturers to test their designs thoroughly before committing to large-scale manufacturing, reducing risks and improving product performance. While challenges such as tooling costs and design limitations exist, advancements in die casting technology continue to enhance the efficiency and quality of prototype production. By choosing the right manufacturing partner and leveraging modern die casting techniques, businesses can develop superior products and stay ahead in a competitive market. Die casting prototypes remain a cornerstone of innovation, enabling industries to create reliable and high-performance components that meet the demands of today’s evolving market.